Beamsplitter Cubes: Key Cubic Structural Elements in Optical Systems
Apr. 29, 2025
Beamsplitter cube is a precision optical element based on the design of the cubic structure, which is mainly used to split the incident light into two beams of transmitted and reflected light in a specific ratio. Its unique cubic shape not only gives it compact and stable physical properties, but also makes it play an important role in laser technology, precision measurement, medical instruments, and other fields.
一、Physical Properties and Core Functions of Cubic Structures
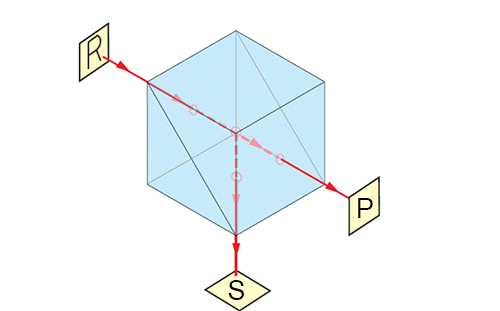
The beamsplitter cube consists of two right-angled prisms bonded together by an interference coating or dielectric coating on the beveled surface to form a typical cube structure. This design allows the optical axes of transmitted and reflected light to be strictly perpendicular or parallel to each other, avoiding the beam shift problems that can result from conventional beamsplitters. The compact form of the cube (typically with side lengths ranging from 5 to 50 mm) makes it easy to integrate into complex optical systems while providing high mechanical stability. In addition, the optical coating technology inside the cube (e.g., polarized beamsplitter, non-polarized beamsplitter) determines its beam-splitting performance, e.g., Polarized Beamsplitter Cubes (PBS) can efficiently separate S-polarized and P-polarized light.
二、Spectral mechanisms in cubic structures
The core principle of the beamsplitter cube relies on the spectral coating layer inside its cube. When light enters the cube, the coating layer splits the light beam in a preset ratio according to the wavelength, polarization state or angle of incidence of the light:
Polarized beam splitting: In the polarized beam splitting cube, the coating layer is designed to reflect S-polarized light (vibration direction perpendicular to the incident plane) and transmit P-polarized light (vibration direction parallel to the incident plane) through a multilayered dielectric film design, with polarization extinction ratios of up to 1000:1 or more.
Non-Polarized Beamsplitting: The coating layer of Non-Polarized Beamsplitting Cube (NPBS) splits non-polarized light uniformly, e.g., 50:50 splitting ratio, which is commonly used in interferometers or optical path balancing systems.
Optical Path Coherence: The cube structure ensures that the transmitted and reflected light have the same optical path, a feature that is critical in interferometry or quantum optics experiments.
三、Classification: Types of beam splitting based on the cube structure
Based on the spectral splitting mechanism and coating characteristics, spectral splitting cubes can be classified into the following categories:
1. Polarized beam-splitting cubes (PBS)
Cubic structures with polarization-sensitive coatings are widely used in laser projectors, fiber-optic communications, and other scenarios that require polarization state control. For example, in a 3LCD projector, the PBS cube is responsible for separating the polarization states of red, green, and blue light.
2. Non-Polarized Beam Splitting Cube (NPBS)
The coating layer achieves a fixed ratio of non-polarized light (e.g., 30:70 or 50:50), and the cube structure ensures a stable angle of separation, which is suitable for medical equipment such as optical coherence tomography (OCT).
3. Depolarizing Spectroscopic Cube (DPBS)
The specially designed cube structure eliminates polarization dependence and is used in optical communication systems to split optical signals of different wavelengths and avoid polarization mode dispersion problems.
4. Broadband beam splitter cube
By optimizing the coating layer material and structure, the cube can cover a wide spectral range from UV to IR (e.g., 350-1600nm), which is suitable for spectrometers or multi-wavelength laser systems.
五、Multi-disciplinary applications of the Beamsplitter cube
1. Laser technology
Beam Control: Used in laser systems to separate or combine beams of different polarization states (e.g. laser processing, fiber optic communications).
Intense laser system: High damage threshold beam splitting cube is suitable for high power lasers to reduce photothermal effect loss.
2. Optical measurement
Precision instruments: non-polarized beam splitting in interferometers and microscopes to reduce measurement errors (e.g., depolarizing beam splitting cube for environmental monitoring equipment).
Spectral analysis: combined with spectroscopic prisms or gratings for multi-wavelength spectral separation and detection.
3. Medical and Industrial Inspection
Life science: used in fluorescence microscope, flow cytometer and other equipment for optical path beam splitting, to achieve multi-channel imaging.
Industrial quality inspection: Split the light source and detection optical path in material composition testing and food safety analysis to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio.
4. Scientific research and communication
Optical communication system: depolarization beam splitting cube is used to eliminate the polarization dependence of signal light and improve communication stability.
Quantum optics: separating photon paths in quantum entanglement experiments to support quantum state regulation