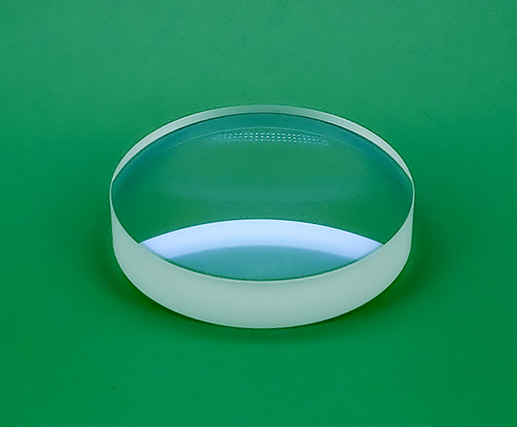
Barium Crown Glass
In the design and manufacture of optical systems and lenses, in order to obtain good optical performance, it is often necessary to use optical glasses with a high refractive index and low dispersion. For example, in order to produce a desirable multifocal ophthalmic lens formed by fusing a high index glass segment with a low index glass blank, the glass used for the segment should preferably have a relatively high index of refraction to reduce the thickness and relative thickness of the lens. Lower dispersion to eliminate annoying color fringing around images produced by the lens. Although barium crown glass from CLZ Precision Optics has been produced with an index of 1.53-1.61 and a reciprocal relative dispersion of 40-64, as shown in Greek letter 11 (nu), this glass is not chemically stable but tends to stain and tarnish, thereby damaging optical properties of lenses made therefrom. In addition to the requirements for refractive index, dispersion, and stability, barium crown glass must have high expansion and low softening point in order to fuse portions of this glass to the crown glass blank to make multifocal lenses.
Barium Crown Glass is referred to as BaK glass or crown glass. The refractive index and density are between K and ZK glass. Crown glass is basically a borosilicate glass containing barium, zinc, potassium, and sodium. It contains a lot of barium, and the mass fraction of the sum of BaO and ZnO is about 20%-40%. Mainly used as a material for optical parts in optical instruments, such as optical lenses, prism and Cylindrical lenses.
By modifying the glass formula, the optical glass without lead, arsenic and cadmium and other radioactive elements is expressed by a prefix "H-" indicating its envioronment-friendly characteristics, for example: H-BaK6
- Spherical Lenses
- Optical Dome
- Cylindrical lenses
- Optical Windows
- Optical Prisms
- Optical Mirrors
- Optical Filters
- UV and IR Optics
- Custom Optics
- Optical Coatings
- Blank Material